SMS Network Architecture and Internal Protocols
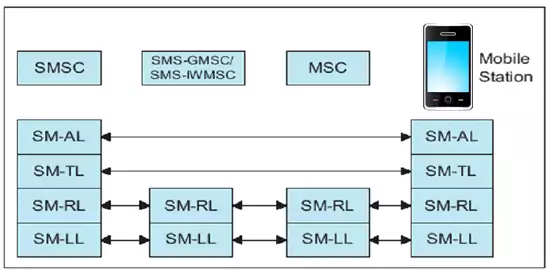
In the SMS network operated by GSM service providers four layers of transport are used (Figure 1.):
SM-AL (Application Layer)
SM-TL (Transfer Layer)
SM-RL (Relay Layer)
SM-LL (Lower Layers)
Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway is located in the SM-AL layer. When sending an SMS message, the software creates protocol data units (PDUs) transported by the SM-TL layer. When a GSM device attached to the PC receives an SMS message, the message is also encoded according to the SM-TL layer PDU specification. Ozeki NG - SMS Gateway decodes this PDU and makes the message readable for computer programs and computer users.
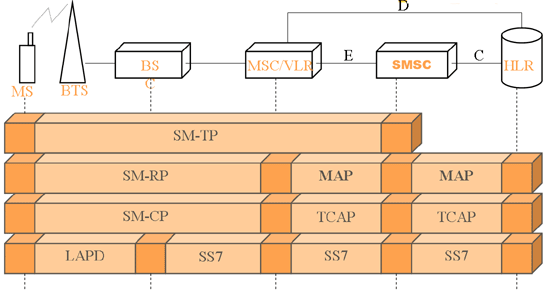
To understand how the SMS travels from the mobile phone to the SMSC, look at Figure 2 below. In this figure you can see which protocols are used and which GSM network entities take place in the communication process. As you can see, the mobile phone (Mobile station) transmits the SMS message to the GSM base station (BTS) through a wireless link. Then the message goes through the backbone network of the service provider. The Mobile Switching Centre (MSC), the Home Location Register (HLR) and, optionally, the Visitor Location Register (VLR) is used to find out the appropriate Short Message Service Centre (SMSC) which will store and forward the message when the receiving party becomes available.